一些最近遇到的广度搜索算法题
几道广度搜索算法
最近在看算法然后就看见了几道BFS的算法题,之前对于算法学的并不好,基本全忘了,正好用着复习一下
方块问题
在一个4行4列的平面立面,有7个红色块8个蓝色块和一个白色块,你只能移动白色的快,当移动后,白色块会和被移动的块交换位置。
使用上下左右来记录白色块的交换顺序,问:最少需要多少步能让图形从S变为T
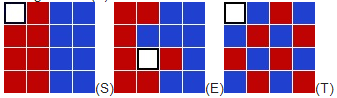
分析:一开始看见这个题目是没有什么思路的,看了提示用BFS,然后采取把BFS相关算法介绍看了一下,才大概有个思路,通过广度搜索暴力求解答案。
因为图比较小,所以花的时间并不是太多。简单的说就是模拟所有可能路径找到最短的那条。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35def exchange(status, p1, p2):
# 交换P1 P2,
small=p1 if p1<p2 else p2
big=p2 if p2>=p1 else p1
return status[:small]+status[big]+status[small+1:big]+status[small]+status[big+1:]
def go(node):
# path: 到达目前状态的路径
# cursor: 可移动块所处的位置
# status: 当前状态
(path, cursor, status) = node
if cursor == 0 and status == '2101101001011010':
print(path)
if status in visited:
return
visited[status] = True
if cursor + 4 < 16: # go down
patterns.append((path + "D", cursor + 4, exchange(status, cursor, cursor + 4)))
if cursor - 4 > -1: # go up
patterns.append((path + "U", cursor - 4, exchange(status, cursor, cursor - 4)))
if cursor % 4 < 3: # go right
patterns.append((path + "R", cursor + 1, exchange(status, cursor, cursor + 1)))
if cursor % 4 > 0: # go left
patterns.append((path + "L", cursor - 1, exchange(status, cursor, cursor - 1)))
patterns = [("", 0, '2011001100110011')]
visited = {} # 保存到达过的状态
count = 0
while (count < len(patterns)):
if go(patterns[count]):
break
count += 1
当然如果用位运算应该效率更高,不过因为不擅长位运算就不用位运算了。
二叉树宽度
定义二叉树的宽度为二叉树中包含节点最多的层中的节点数。现有一颗二叉树,其深度不大于 N
基本结构为
typedef struct tree
{
struct tree left;
struct tree right;
} * Btree
求二叉树宽度, ROOT 为此二叉树根节点指针
分析:BFS简单的概念题,二叉树搜索,循环遍历每一层的节点,计算出个数,输出一个最大值即可1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44class Node:
def __init__(self):
self.left = None
self.right = None
def max_width(root):
if not root:
return 0
arr1 = []
arr2 = []
arr1.append(root)
ans = 1
while len(arr1) > 0:
arr2 = []
for node in arr1:
if node.left:
arr2.append(node.left)
if node.right:
arr2.append(node.right)
ans = max(ans, len(arr2))
arr1 = arr2
return ans
n1 = Node()
n2 = Node()
n3 = Node()
n4 = Node()
n5 = Node()
n6 = Node()
n7 = Node()
n8 = Node()
n9 = Node()
n0 = Node()
n1.left = n2
n1.right = n3
n2.left = n4
n2.right = n5
n4.right = n6
n5.left = n7
n5.right = n8
n3.right = n9
n3.left = n0
print max_width(n1)
print max_width(n2)
和BFS无关的一道题
搜狐员工小王最近利用假期在外地旅游,在某个小镇碰到一个马戏团表演,精彩的表演结束后发现团长正和大伙在帐篷前激烈讨论,小王打听了下了解到, 马戏团正打算出一个新节目“最高罗汉塔”,即马戏团员叠罗汉表演。考虑到安全因素,要求叠罗汉过程中,站在某个人肩上的人应该既比自己矮又比自己瘦,或相等。 团长想要本次节目中的罗汉塔叠的最高,由于人数众多,正在头疼如何安排人员的问题。小王觉得这个问题很简单,于是统计了参与最高罗汉塔表演的所有团员的身高体重,并且很快找到叠最高罗汉塔的人员序列。 现在你手上也拿到了这样一份身高体重表,请找出可以叠出的最高罗汉塔的高度,这份表中马戏团员依次编号为1到N。
输入描述:
首先一个正整数N,表示人员个数。
之后N行,每行三个数,分别对应马戏团员编号,体重和身高。
输出描述:
正整数m,表示罗汉塔的高度。
输入例子:
6
1 65 100
2 75 80
3 80 100
4 60 95
5 82 101
6 81 70
输出例子:
4
分析:这个题目我觉得挺有趣的,主要是身高体重2列,排序好身高然后就需要比较体重。搜了一下发现是一个最长上升子序列长度的问题。现在的问题就变成了找体重的最长子序列就可以了。
最长子序列可以开一个栈,每次取栈顶元素top和读到的temp元素做比较,如果temp>top就把temp入栈,如果temp<top就二分查找栈中比temp大的第一个数并用temp替换它。最长子序列即为栈的大小。参考
1 | def lcs(nums): |